- About
- Our Clinics
- Patient service categories
- Family Medicine
- Musculoskeletal Health
- Mental Health
- Specialist Medicine
- Pregnancy & Midwifery
- Women's Health
- Paediatrics
- Wellness
- Packages
- Resources
- Contact
- Insurance
- Store
Women’s Services

Women are recommended to have a general check-up with their doctor every year to ensure health and to pick up any early warning signs of disease or illness. The screening tests and frequencies of tests advised will change as you age, such as mammograms and pap smears. Our comprehensive range of women’s health services ensures that we address all aspects of your health and well-being, relevant to your individual needs. You can check with your doctor for specific recommendations based on your medical situation or choose from the packages listed further down the page.
There are some conditions that pose more risk to women, and therefore need to be monitored and screened for. Many diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes and some cancers can be identified in their early stages, when treatment is often more effective. Browse our service offerings:
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix. Most cervical cancers are caused by various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Pap smears are an effective screening measure for women against cervical cancer. Among females in Hong Kong, cervical cancer has been the seventh commonest cancer.
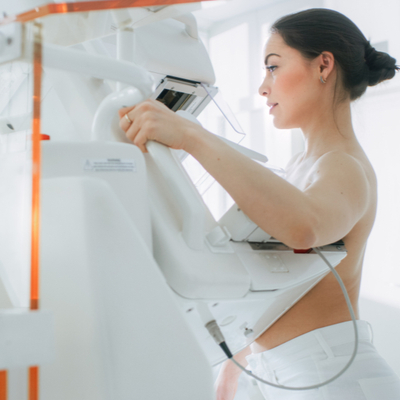

The Hong Kong Breast Cancer Foundation recommended the following:

Pap smears, also known as the Pap test, are an effective preventative measure for women against cervical cancer. According to the World Health Organization, the Pap smear is the only test used in large populations that have been shown to reduce cervical cancer incidence and mortality. This article aims to answer many of the common questions and concerns regarding Pap smears..read more
A mammogram is a non-invasive, specialised medical imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to see inside the breasts.
During a mammogram, the breasts are gently flattened between two plates of the x-ray machine to spread the breast tissue apart gently. Breast images are then taken to check for abnormalities.
Compression holds the breast in place to minimise blurring and evens out the shape of the breast to reduce the radiation dose required...read more
A breast ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique technique that creates detailed images of the breast tissue. This diagnostic procedure is performed to examine the internal structures of the breast, identify abnormalities or changes, and aid in the diagnosis of breast conditions.
Breast ultrasound is commonly used in conjunction with mammography, as it provides additional information that might not be visible on a mammogram.
Reasons for women to get a breast ultrasound include:
A pelvic ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that generates detailed images of the structures within the pelvic region.
This diagnostic tool is used to examine the organs and tissues of the lower abdomen, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder in women.
Pelvis ultrasound aids in the identification of abnormalities, assists in diagnosing various conditions, and guides treatment decisions. It is commonly used for assessing reproductive health, evaluating urinary problems, and detecting masses or cysts.
A lipid profile is a blood test that measures the levels of various lipids (fats) in the bloodstream.
It is essential for assessing an individual's risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues.
It also helps healthcare professionals recommend appropriate lifestyle changes, medications, or treatments to manage lipid levels and maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
TSH, or thyroid-stimulating hormone, is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. TSH plays a crucial role in regulating the thyroid gland, which is responsible for producing hormones that control the body's metabolism, growth, and development. The primary function of TSH is to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce and release the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
A TSH test is included in a well-woman package to evaluate thyroid function and screen for potential thyroid disorders. The test measures the level of TSH in the blood, which can help doctors determine whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive.
Thyroid issues are more prevalent in women than in men. The exact reasons for this disparity are not fully understood, but hormonal differences and genetic factors are believed to play a significant role. Women's hormonal changes during various life stages, such as pregnancy, postpartum, and menopause, can affect thyroid function and make them more susceptible to thyroid disorders.
Early detection and appropriate treatment of thyroid issues are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Therefore, it is crucial for women to be aware of their increased risk and discuss thyroid screening with their healthcare providers during routine check-ups or well-woman visits.
Glucose, fasting refers to a blood test that measures the levels of glucose in the blood after a short period of fasting. It is a common diagnostic tool used to screen for, diagnose, and monitor diabetes or pre-diabetes.
Fasting is required as this is when the body uses stored glucose from the liver to maintain normal blood sugar levels. The blood glucose levels of a healthy individual remain relatively stable during fasting, while people with diabetes or pre-diabetes may have elevated fasting blood glucose levels.
While there is no inherent gender-based difference in the risk of developing abnormal blood glucose levels, some specific factors can increase the risk for women.
Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after giving birth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is associated with insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can cause fluctuations in blood glucose levels and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes among women.
Ferritin is a protein found in cells that stores and releases iron as needed. Measuring ferritin levels in the blood provides information about the body's iron stores, helping doctors to detect iron deficiency or overload.
A ferritin test is included in a well-woman check-up because women are at a higher risk of developing iron deficiency anaemia due to blood loss during menstruation and increased iron requirements during pregnancy.
CA125 is short for Cancer Antigen 125. This is a protein found in the blood that is often used as a tumour marker. Elevated levels of CA125 can be associated with certain cancers, particularly ovarian cancer. However, CA125 levels can also be elevated in non-cancerous conditions, such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and uterine fibroids, as well as during menstruation or pregnancy.
Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption and maintaining bone health.
Women, especially postmenopausal women, are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis (a condition characterized by weakened bones) compared to men. Adequate vitamin D levels help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Hormonal changes during various stages of a woman's life, such as menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can affect vitamin D metabolism and levels.
Given the importance of vitamin D in various aspects of women's health, testing for vitamin D levels can help doctors identify deficiencies and recommend appropriate supplementation or lifestyle modifications.
A urine dip is a quick and simple diagnostic tool used to analyse a urine sample for the presence of various substances, such as glucose, protein, red and white blood cells, and nitrates. The test involves dipping a specially designed strip with chemical reagents into a urine sample. The reagents on the strip react with the urine and change colours if certain substances are present, indicating potential health issues.
A urine dip is included in a well-woman package as it can help detect the presence of white blood cells, nitrites, or bacteria, which may indicate a urinary tract infection. UTIs are more common in women than in men, and early detection is crucial for timely treatment and prevention of complications.